Introduction
Internet Protocol Television, commonly known as IPTV, is rapidly gaining attention as a formidable alternative to conventional cable and satellite TV services. Unlike traditional broadcasting methods, where television programming is delivered via cable or satellite systems, IPTV utilizes the infrastructure of broadband internet networks to stream television content directly to viewers. This cutting-edge technology seamlessly integrates with the growing trend of on-demand entertainment, providing unprecedented flexibility and diverse content options to users worldwide.
The rising popularity of IPTV has sparked numerous discussions and questions among potential subscribers and tech enthusiasts. One of the most intriguing and frequently asked questions is whether IPTV can function without an internet connection. Given that IPTV is fundamentally grounded on internet-based protocols, this query challenges the core understanding of how the service operates. Nonetheless, it is crucial to delineate the intricacies involved to ascertain the feasibility of using IPTV without the internet.
This blog post aims to unravel the complexities surrounding this question. Over the course of the discussion, we will delve into the technical requirements of IPTV, explore possible misconceptions, and examine various scenarios to determine if there exists any potential for enjoying IPTV services devoid of an internet connection. By shedding light on these aspects, we aspire to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of IPTV’s dependency, or lack thereof, on internet connectivity. Dive in as we unveil the surprising truth about IPTV and its relationship with the internet.
Can You Use IPTV Without Internet? Understanding the Basics

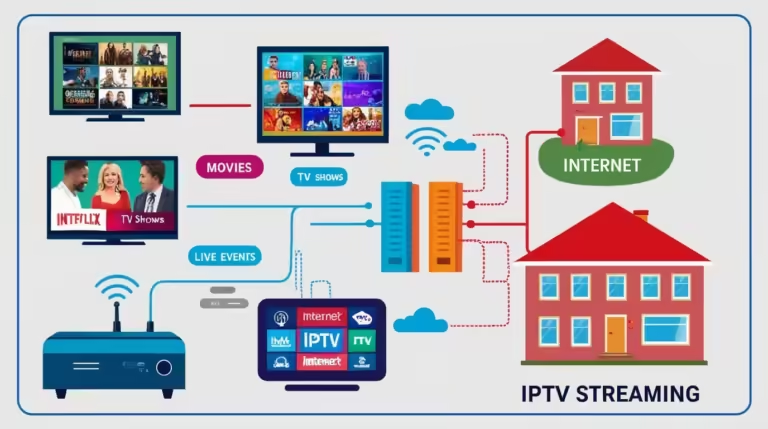
Internet Protocol Television, commonly referred to as IPTV, is a technology that allows the delivery of television content over internet protocols. Unlike traditional broadcast and cable TV formats, IPTV does not rely on satellite signals or cables to deliver content. Instead, it uses your existing internet connection to stream live TV channels, on-demand videos, and other multimedia content straight to your device.
Generally, IPTV works by converting television signals into data packets, which are then transmitted over the internet. Once these packets reach your device, a specialized IPTV application or device interprets the data and displays the content in real time. This method ensures that the content can be delivered seamlessly, provided the internet connection is stable and fast.
One of the critical aspects for the smooth functioning of IPTV is a reliable internet connection with adequate bandwidth. Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted per second, and a higher bandwidth allows more data to be streamed without interruption. For high-definition (HD) content, a minimum of 5 Mbps (megabits per second) is generally recommended, while 25 Mbps or higher is ideal for ultra-high-definition (UHD) or 4K content.
The speed and stability of the internet connection also play a crucial role. A throttled or intermittent connection can lead to buffering, reduced quality, and an overall subpar viewing experience. Therefore, ensuring you have a dependable internet service provider (ISP) is vital when using IPTV services.
Examples of common IPTV services include subscription-based solutions like Hulu, YouTube TV, and Sling TV. These services are designed to be straightforward, requiring only a subscription and a device with internet access. Free IPTV options also exist but often come with legal and quality concerns.
In summary, while IPTV relies heavily on a stable and fast internet connection for optimal performance, its ability to provide a vast array of content seamlessly makes it a popular choice for many users seeking an alternative to traditional television formats.
How IPTV Typically Relies on Internet Connectivity

Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) predominantly relies on internet connectivity to function effectively. This reliance stems from the fundamental manner in which IPTV transmits data. Unlike traditional broadcast methods, IPLV delivers content in the form of data packets over the internet. These packets traverse through various networks to reach the end user’s device, where they are reassembled to provide seamless video and audio streams.
The process hinges on several critical streaming protocols. Notably, HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) are favored for their ability to adapt video quality in real-time based on the user’s current internet speed. HLS, for instance, splits the stream into small segments and adjusts the quality dynamically, ensuring a smooth experience even when network conditions vary. Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), on the other hand, is often used for live streaming, requiring a stable internet connection to minimize latency and buffering.
The role of servers in this ecosystem cannot be overstated. IPTV providers host content on databases that are accessed through servers. When a user selects a channel or stream, a request is sent to these servers, which then fetch and deliver the content back to the user’s device. This entire transaction necessitates robust internet connectivity. Without internet access, these requests cannot be made, rendering the IPTV service non-functional.
Technical limitations present significant challenges when attempting to stream IPTV without a strong internet connection. High-resolution streams, such as 4K content, consume substantial bandwidth; without adequate internet speed, buffering and lowered quality are inevitable. Disruptions in connectivity can lead to interrupted or frozen streams, significantly detracting from the user experience. Therefore, to leverage the full potential of IPTV, a dependable and high-speed internet connection is indispensable.
The Role of Offline Content: Can You Use IPTV Without Internet Access?

In today’s digital age, the idea of accessing television programming without an internet connection may seem counterintuitive. However, some IPTV services have adapted to consumer needs by incorporating the feature of offline content. This innovation allows users to download episodes, movies, or other types of media to their devices, enabling playback without an active internet connection.
A few IPTV providers have harnessed this capability, offering their subscribers the convenience of offline viewing. For instance, leading services such as Netflix and Amazon Prime Video allow their users to download select content directly to their devices. This feature has extended the IPTV experience beyond the constraints of an internet connection, providing flexibility for those who have intermittent or limited access to the web.
The prime advantage of offline content is the ability to enjoy media anywhere and anytime, irrespective of internet availability. For frequent travelers, commuters, or individuals residing in areas with poor internet connectivity, this feature is particularly valuable. By pre-downloading desired shows or movies, viewers can ensure uninterrupted entertainment during flights, road trips, or areas with limited network coverage.
Though advantageous, the use of offline content does come with its set of limitations. Storage capacity is a primary concern. Downloading high-definition content requires significant space, and most devices might struggle to accommodate large libraries. Additionally, downloaded content often comes with an expiry date. IPTV providers mandate that media must be re-verified through an internet connection after a certain period, commonly ranging from 30 days to a few months. This measure ensures licensing agreements and content rights are upheld.
Moreover, not all content available on an IPTV platform is eligible for download. Restrictions based on licensing agreements mean that only select titles may be available for offline viewing, which can limit the user experience. Nonetheless, the growing trend towards offline capabilities within IPTV services represents a proactive step towards accommodating diverse user needs and combating connectivity challenges.
Alternative Methods: Streaming IPTV Without an Internet Connection
Exploring alternative methods to stream IPTV without a traditional internet connection brings us to the concept of local network streaming. Local network streaming utilizes local network infrastructure, essentially delivering content directly from a media server within your home network, rather than relying on an external internet connection. Technologies such as Plex and Emby have made this increasingly viable.
Plex and Emby are popular media server solutions that enable users to store their digital content—such as TV shows, movies, and live TV broadcasts—on a dedicated server within their home. These services then stream the content to various devices, like smart TVs, tablets, or smartphones, over the local network. Setting up media servers like Plex and Emby generally involves installing server software on a compatible device, configuring the server to organize and manage your media library, and ensuring all client devices are correctly connected to the local network.
In order to set up a Plex or Emby server, a user will need certain hardware, such as a computer, NAS (Network Attached Storage) device, or even some high-end routers that support these server functionalities. The setup also requires the necessary software, which is typically free for basic use, though premium features may incur additional costs.
When evaluating the practicality of these local streaming methods for the average user, several factors emerge. Firstly, while these solutions do circumvent the need for an internet connection for media delivery, they come with their own requirements and complexities. Technical know-how is necessary to set up and maintain the server and ensure seamless connectivity across devices. Additionally, the initial cost of required hardware might deter some users from adopting such methods.
While local network streaming can be a compelling way to enjoy IPTV and other digital content without an internet connection, it may not be feasible for everyone. The setup complexity and associated costs need to be weighed against the benefits of bypassing traditional internet usage for streaming media. Ultimately, for tech-savvy individuals, these methods present a viable alternative, though the average user may find it less straightforward.
Expert Opinions: Is It Really Feasible to Use IPTV Without the Web?
In the ever-evolving landscape of television broadcasting, the question of whether IPTV can function without internet connectivity has sparked considerable debate among industry experts. It appears that while the idea may sound appealing, the practicality of such a setup is more complex.
According to John Harris, a senior technical consultant at Streaming Tech Solutions, “IPTV fundamentally relies on internet Protocols to deliver content. It is hard to imagine a scenario where IPTV can bypass the necessity of an internet connection.” This aligns with the general consensus that internet connectivity is crucial for the seamless functioning of IPTV services.
Another perspective comes from Lisa Chen, a project manager at NetStream Media. Chen points out, “In traditional terms, IPTV systems were designed to use local networks to stream content. However, even these local networks usually have to connect to broader internet infrastructure, especially for accessing broader ranges of content.” Her view emphasizes that any deviation from established networking protocols could severely limit the content availability and user experience.
From a service provider’s standpoint, Alex Kumar, a representative from WorldStream IPTV, states, “Though there have been attempts to create offline IPTV solutions, these typically rely on pre-downloaded or cached content, which still initially requires an internet connection.” This insight highlights that while offline IPTV might circumvent continuous internet use, it does not completely eliminate the initial dependency.
In the realm of users, opinions are varied but commonly lean towards necessity. Susan Wilkins, an avid IPTV user, mentions, “Without an internet connection, you lose the core essence of what makes IPTV versatile and comprehensive. Even with local content storage, updates and new channel integrations need the internet.”
In analyzing these diverse views, one can see that common misconceptions about the offline utility of IPTV often overlook the intrinsic link between IPTV and internet technology. While theoretically, IPTV could work in a limited offline environment through local servers or preloaded content, the essence of its functionality and access to a dynamic range of content still significantly relies on continual internet connectivity.
Real-World Scenarios: Using IPTV Without Internet
In remote areas without reliable internet access, IPTV users often face challenges in maintaining a seamless viewing experience. However, various real-world scenarios illustrate how innovative measures and technology adaptations can allow IPTV to function effectively without a direct internet connection.
For instance, in rural communities with intermittent or limited internet services, local providers sometimes establish dedicated IPTV networks. These networks utilize satellite connections to receive content, which is then distributed locally through a closed-loop system. This setup bypasses the need for a robust internet connection while still delivering high-quality IPTV services. Despite potential latency issues, this solution often proves effective, ensuring that users in these areas do not miss out on entertainment options.
Another scenario involves frequent travelers, such as RV owners or individuals on long-term remote assignments. For such users, advanced portable satellite devices have become invaluable. These devices can access IPTV channels via satellite signals even in areas without cell reception or Wi-Fi. Travelers often equip their vehicles with compact satellite dishes paired with pre-loaded content on IPTV boxes. This combination ensures a continuous streaming experience, regardless of internet availability, albeit with a dependence on satellite signals which can be affected by weather conditions.
In urban settings, some users mitigate poor internet connections by downloading IPTV content during periods of stable connectivity. Many IPTV providers now offer options to download shows and movies for offline viewing. This feature allows users to curate a library of content that they can access without needing an active internet connection, bridging gaps during intermittent internet availability.
These adaptations highlight the versatility and resilience of IPTV technology. By leveraging satellite connections, pre-loaded content, and dedicated local networks, it becomes possible to enjoy IPTV services even in the absence of a stable internet connection. Such innovative solutions demonstrate the industry’s capacity to meet the needs of diverse user groups, ensuring continuous access to entertainment across a variety of challenging scenarios.
Tech Innovations: The Future of IPTV Without Internet
Technological advancements are constantly evolving, paving the way for innovative solutions that might make IPTV less dependent on traditional internet connections. One compelling direction for the future of IPTV is satellite-based internet services. These services have the potential to provide high-speed and reliable connectivity to even the most remote areas where traditional internet infrastructure might be lacking. Companies like SpaceX and OneWeb are at the forefront of developing low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations. These constellations aim to deliver internet services with low latency and high bandwidth, thereby making IPTV more accessible.
Another pivotal development is the emergence of 5G technology. 5G promises to revolutionize not only mobile internet speeds but also the way data is transmitted and received across devices. With its ultra-low latency and higher capacity, 5G could drastically enhance the IPTV experience. Users might witness a significant reduction in buffering times and an increase in video quality. This technology could even support seamless streaming in 4K or higher resolutions, thereby setting a new standard for user experience.
In addition to these connectivity solutions, advancements in offline data storage and compression techniques are equally promising. Researchers are continuously exploring new ways to store large amounts of video content within smaller, more efficient formats. This could enable devices to pre-download and store IPTV content locally, reducing the dependency on continuous internet streams. Techniques like High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) and the emerging Versatile Video Coding (VVC) could play a substantial role in this evolution by enhancing compression rates without sacrificing quality.
Ongoing research and development in the telecom and broadcasting industry indicate that the future of IPTV is likely to be greatly influenced by these technologies. As these innovations mature, users can expect a richer, more seamless viewing experience with fewer interruptions and unprecedented access to content. While the internet will likely remain a significant component of IPTV delivery, these technological advancements suggest a future where IPTV could operate efficiently with minimal reliance on traditional internet connectivity.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we have delved into the fascinating question of whether IPTV can function without an internet connection. As we have discussed, traditional IPTV services fundamentally rely on an internet connection to transmit live television signals or stream content on demand. This dependency on the internet is one of the core attributes that distinguishes IPTV from other forms of television broadcasting.
However, we also explored some alternative methods that might allow for partial use of IPTV services without a continuous internet connection, such as utilizing pre-downloaded content or relying on local network setups. Despite these workarounds, it is essential to understand that they only offer a limited experience compared to the full scope of IPTV services, which include real-time streaming, live broadcasts, and interactive functionalities that are inherently linked to an active internet connection.
Given the current technological landscape, the integration of internet connectivity with IPTV remains vital. As innovations and technology evolve, there is potential for new methodologies and improvements that may enhance or even modify the current prerequisites. Staying informed about such advancements is crucial for users who wish to leverage the full benefits of IPTV.
As we have underscored, while there are fragmentary means to use IPTV without internet, these are not comprehensive solutions. The predominant reliance on internet connectivity is an aspect that users must consider.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with IPTV, especially if they have explored unconventional ways to utilize the service. Your feedback and insights are invaluable and may shed light on additional possibilities that others may find beneficial.