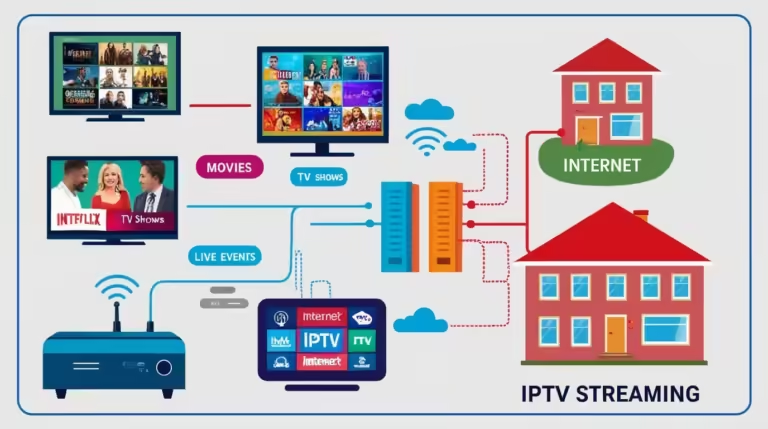
In today’s digital age, the way we consume television is undergoing a radical transformation. Traditional cable is being outpaced by Internet Protocol Television (IPTV), which delivers content over the internet rather than through conventional broadcast or satellite methods. But have you ever wondered, “Which network is used for IPTV?” Understanding the network behind IPTV is crucial for anyone who wants to grasp how streaming services work, ensure optimal viewing experiences, and make informed decisions about their media consumption. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the networks that power IPTV, unravel the technology behind them, and help you choose the best option for your streaming needs.
IPTV Exposed: Which Network is Used for Seamless Streaming?
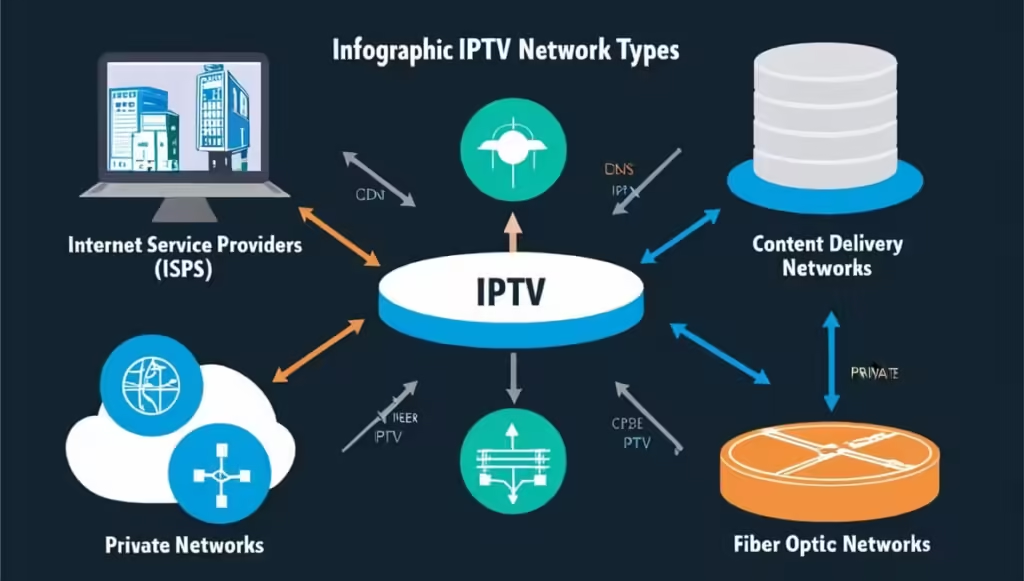
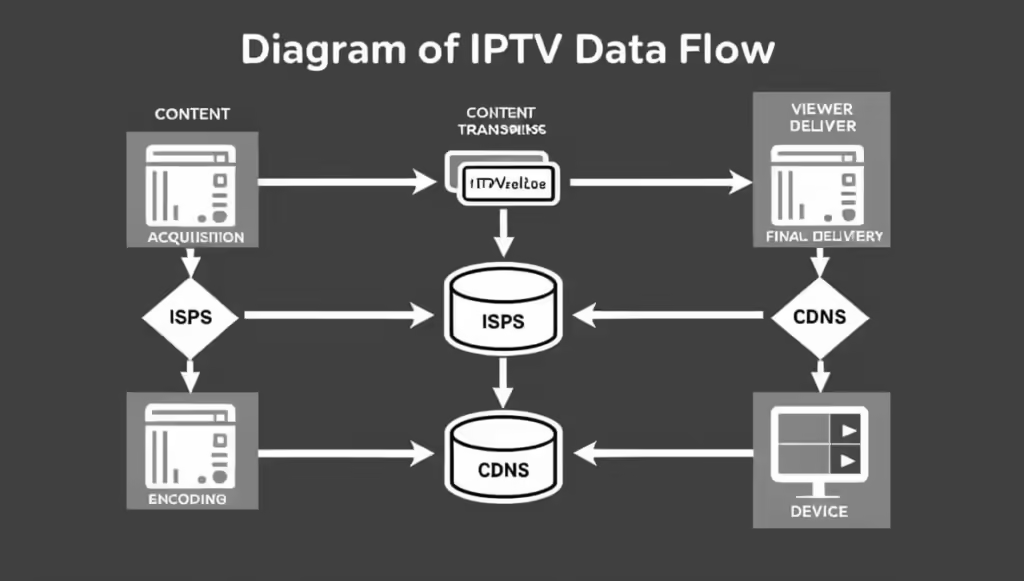
IPTV is all about delivering television programming through IP networks. But to answer the question, “Which network is used for IPTV?” we need to dive into the backbone of this technology. Essentially, IPTV relies on a network infrastructure capable of handling large amounts of data quickly and reliably. This means that several types of networks can be involved:
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): The most common network used for IPTV is the one provided by your ISP. Major ISPs have robust infrastructure to support high-speed data transfer, which is essential for streaming live and on-demand content without interruptions. ISPs use high-bandwidth networks, such as fiber-optic connections, to deliver IPTV content effectively.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): For seamless streaming, IPTV providers often use CDNs. CDNs are distributed networks of servers that cache content closer to the end-user. By minimizing the distance data travels, CDNs reduce latency and improve the streaming experience. Popular CDNs include Akamai, Cloudflare, and Amazon CloudFront.
- Private Networks: Some IPTV providers maintain their own private networks to ensure high-quality streaming. These networks are optimized for delivering content with minimal delays and interruptions, offering an enhanced viewing experience compared to standard internet connections.
- Fiber Optic Networks: Fiber optic networks are increasingly used for IPTV due to their high-speed data transfer capabilities. Fiber optics use light to transmit data, allowing for faster and more reliable streaming compared to traditional copper cables.
How IPTV Works: Which Network is Used for Reliable Data Delivery?
To understand “Which network is used for IPTV?” and how it ensures reliable data delivery, let’s break down the process of IPTV delivery:
- Content Acquisition: IPTV providers acquire content from various sources, including broadcasters, studios, and content creators. This content is then encoded into a digital format suitable for streaming over IP networks.
- Content Delivery: The encoded content is sent through a network, often a combination of CDNs and ISP networks, to reach viewers. The network infrastructure must handle high volumes of data and manage traffic efficiently to maintain streaming quality.
- Data Compression and Transmission: Data compression techniques are used to reduce the size of the content without compromising quality. This compressed data is transmitted over the internet or private networks to the end-user. The network’s capability to handle this data efficiently is crucial for avoiding buffering and ensuring smooth playback.
- Decoding and Playback: Once the content reaches the viewer’s device, it is decoded and displayed. The reliability of the network impacts how quickly and effectively the content is decoded and shown on the screen. High-speed, low-latency networks are vital for a seamless viewing experience.
- Network Quality and Performance: The quality of the network used for IPTV directly influences data delivery reliability. Networks with higher bandwidth and lower latency offer better streaming experiences, reducing buffering and improving overall satisfaction.
Network Providers in IPTV: Which Network is Dominating the Market?
In the competitive landscape of IPTV, several network providers play crucial roles. To determine “Which network is used for IPTV?” and who is leading the market, let’s look at some key players:
- Telecommunication Companies: Major telcos, like AT&T, Verizon, and Deutsche Telekom, offer IPTV services over their extensive broadband networks. These companies invest heavily in network infrastructure to provide reliable and high-quality IPTV services.
- Cable Providers: Traditional cable companies, such as Comcast and Charter, have also entered the IPTV market. They leverage their existing networks and technology to offer IPTV alongside their traditional cable services.
- Dedicated IPTV Providers: Companies like Hulu + Live TV, YouTube TV, and Sling TV operate primarily as IPTV providers. They use a combination of CDNs and ISPs to deliver content efficiently. These providers focus on offering diverse channel lineups and on-demand content through optimized networks.
- Global CDN Providers: Global CDNs, such as Akamai and Cloudflare, support many IPTV services by enhancing content delivery speeds and reliability. They play a critical role in ensuring that IPTV providers can offer smooth and uninterrupted streaming experiences.
- Regional Network Providers: In various regions, local network providers specialize in IPTV. They often build tailored networks to cater to specific regional needs and preferences, ensuring localized content delivery and support.
Evaluating Network Performance: Which Network is Used for Optimal Streaming Quality?
When considering “Which network is used for IPTV?” it’s essential to evaluate network performance to ensure the highest quality streaming experience. Key factors to consider include:
- Bandwidth: Higher bandwidth networks can handle more data simultaneously, which is crucial for streaming high-definition (HD) and 4K content without interruptions. Look for networks that offer high bandwidth capabilities for optimal streaming quality.
- Latency: Low latency networks ensure minimal delay between sending and receiving data. This is important for live streaming and interactive features. Networks with low latency provide smoother, more responsive streaming experiences.
- Jitter and Packet Loss: Jitter refers to the variability in packet arrival times, while packet loss involves the loss of data packets during transmission. Networks with minimal jitter and packet loss deliver more stable and consistent streaming experiences.
- Network Congestion: During peak times, network congestion can impact streaming quality. Networks designed to handle high traffic volumes and reduce congestion are preferable for uninterrupted IPTV experiences.
- Quality of Service (QoS): QoS features prioritize IPTV traffic to ensure that streaming content receives the necessary bandwidth and performance. Networks with strong QoS capabilities provide better streaming quality by managing and prioritizing traffic effectively.
Choosing the Right Network for IPTV: Which Network Should You Consider?
When deciding “Which network is used for IPTV?” and choosing the right network for your needs, consider the following factors:
- Service Provider Reputation: Research the reputation of service providers to ensure they offer reliable and high-quality IPTV services. Look for reviews and ratings to gauge customer satisfaction and performance.
- Network Infrastructure: Evaluate the network infrastructure of potential providers. Opt for networks that use advanced technologies like fiber optics and CDNs to ensure fast and reliable content delivery.
- Availability and Coverage: Ensure that the network is available in your area and provides adequate coverage. Some networks may have regional limitations or varying levels of service quality based on location.
- Pricing and Plans: Compare pricing and plans offered by different IPTV providers. Consider the cost in relation to the quality of service, content offerings, and network performance.
- Customer Support: Choose a provider with responsive customer support to address any issues or concerns related to your IPTV service. Reliable customer support ensures that you can quickly resolve any network-related problems.
Conclusion
Understanding “Which network is used for IPTV?” is key to enjoying a seamless and high-quality streaming experience. From the underlying technologies to the major players in the market, the network that powers your IPTV service impacts everything from data delivery to overall performance. By exploring the various networks involved, evaluating their performance, and making an informed choice, you can enhance your IPTV experience and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of digital entertainment.